AWS for Machine Learning Notes Part 1 - Streaming Real-Time Data with Kinesis
A summary of how to deal with real-time data in AWS. We will cover the Amazon Kinesis service offering including Data Streams, Firehose, Video Streams and Data Analytics.
Over the next several months I will cover various AWS services in the context of Machine Learning. The goal is to summarize the main components and tools in a concise way (e.g. cliff notes), as well as show some hands-on examples. The main reason for doing this is I’m studying for the AWS Certified Machine Learning Specialty Exam. In this first part, we will look at the start of any machine learning adventure: the data! In particular, how to deal with live, streaming data.
Amazon Kinesis
We live in a world where data is constantly being generated, and often the value of that data diminishes rapidly with time. Think of use-cases such as needing to react to financial indicators within milliseconds, aggregating clickstream data to optimize a user’s journey on a website or creating real time dashboards to monitor server cluster performance of an MMORPG.
It’s important therefore to be able to gather, process, evaluate (and sometimes store) that data quickly. Amazon Kinesis is a family of services that offers this functionality. It is made up of 4 main components:
- Kinesis Data Streams (KDS)
- Kinesis Data Firehose (KDF)
- Kinesis Video Streams (KVS)
- Kinesis Data Analytics (KDA)
Let’s look at each individually.
Kinesis Data Streams
Kinesis (Data) Streams is a service that allows us to process data in real-time. It’s fast–once collected it’s able to offload it to a data consumer application (e.g. S3, Lambda, etc) within 70 milliseconds! That’s (literally) faster than a blink of an eye! Try blinking right now. It takes humans 100-400 ms to blink. So assuming a low-end average time of 150ms, in the time it took you to blink, Kinesis did what it needed to do in half the time. Ok I’m getting off topic.
Let’s look at the general structure of how Kinesis Streams are structured.
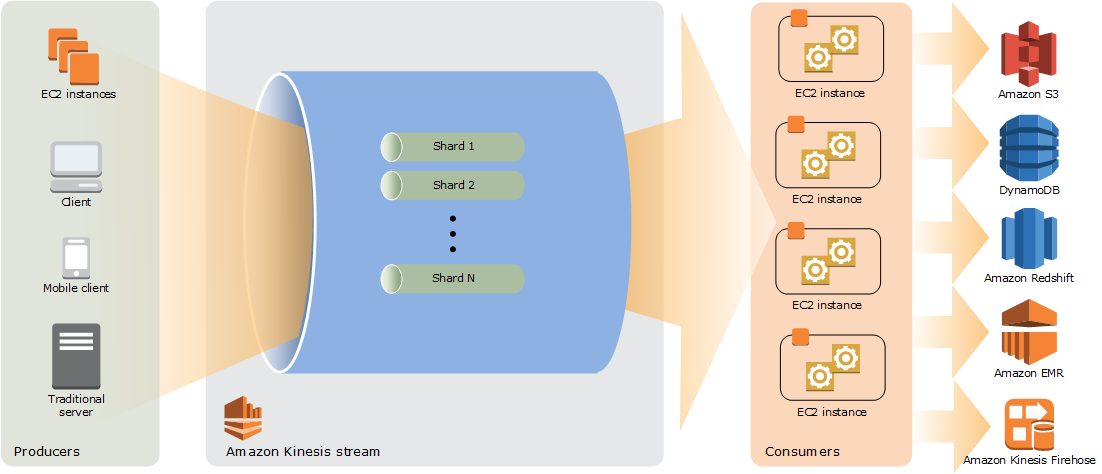
# A more concise way to look at the above:
Data Producers
-> Kinesis Streams (Shards)
-> Data Consumers (EC2, Lambda, KDA, EMR)
-> [Optional] Storage, Analysis (S3, Dynamo, Redshift...)
A typical Kinesis Data Streams application reads data from a data stream as data records. A data stream is a group of data records. Data records are grouped and distributed in shards (see below). Storing data is OPTIONAL with default retention being 24h, extendable to 7 days. Recommended when some action needs to be performed on the data.
Shards
A shard is a collection of data that is sequenced. Using the train example from acloud.guru: if we were to compare a data stream to a train line with trains traveling thousands of miles per millisecond:
- each train is a shard, with its own partition key
- each car of the train is a data record, with its own sequence number
- the passengers in each car are the bytes that make up the data blob. Each car can fit up to 1MB of data.
Useful facts:
- Each shard consists of a sequence of data records. Shards can ingest 1000 records / sec, and support 5 read transactions per second.
- Total bandwidth is therefore
- A data record is the single unit of data (composed of seq number, partition key and blob, up to 1MB)
- Transient data store: retention period 24h (default) to 7 days
- Re-sharding is possible by monitoring producers and consumers via an API call
Kinesis Producer Library (KPL)
- Library to use Kinesis Data Streams and stream data
- automatic and configurable retry mechanism
- processing delay due to higher packing efficiencies / better performance
- Java Wrapper
Kinesis Client Library (KCL)
- Library to consume streams
Kinesis API (via the AWS SDK)
- low level operations and manual configs of the two above
- everything is manually handled (PutRecords, GetRecords)
- no delays in processing
- any AWS SDK (any language, not just Java)
Examples of when to use Kinesis Data Streams:
- Process and evaluate logs immediately
- Run real-time analytics on clickstream data and process it within seconds
- Feed data directly into a ML model
- Real world example: Zillow uses it to collect public record data and MLS listings and update home value estimates in real-time.
Kinesis Data Firehose
- Delivery service for streaming data
- Can support processing tools via Lambda
- Supports Redshift, S3, Splunk
- Supports events (e.g. S3 events to publish to dynamo)
- Kinesis Data Streams as shards and has data retention vs
- Firehose doesn’t have Shards, and storage is primary objective
Examples of when to use Kinesis Firehose:
- Easily collect streaming data from IoT devices, embedded systems, etc
- Run ETL jobs on streaming data
- Processing is optional
- Final destination is S3 or other data store
- Data retention is not important
Kinesis Video Streams
- stream video and images in real time (from security cameras, audio feeds, radar data, etc)
- Continuous and Batch consumers (e.g. EC2) via fragments and frames a.k.a. KVS applications
- Can be stored after or before processing
Examples of when to use Kinesis Video Streams:
- Real time streaming video data
- Batch process and store streaming video
- Feed streaming data into other AWS services
- Ex: Amazon cloud cam -> KVS to EC2 -> identifies person -> sends notification (Lambda) & stores image (S3)
Kinesis Video Analytics
- Continuously read and process data in real-time from KDS or KDF
- Run real time SQL queries (rename columns, joins, etc)
- Store in S3, Redshift, other BI tools
Examples of when to use KDA:
- Run real-time SQL queries on streaming data
- construct apps that provide insight into data
- create metrics, dashboards, monitoring, notifs, alarms
- output query results into S3 or other datasources
- stream ETL jobs
Examples
| Objective | Kinesis service to use | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Stream Apache log files directly from several EC2 instances and store them into Redshift | Kinesis Data Firehose | Kinesis Data Analytics for preprocessing -> Redshift. KDF is for storing streamed data to a final destination. First data is stored to S3 then moved to RS |
| Stream live video coverage of a sporting event to distribute to customers in near real time | Kinesis Video Stream | Process video data and feed into other AWS services (e.g. Streaming EC2 instance or S3 or CloudFront) |
| Transform real-time streaming data and immediately feed into a custom ML application | Kinesis Data Stream | Storing is optional, our primary goal is immediate consumption, transform it and feed it into an ML model |
| Query real-time data, create metric graphs and store output into S3 | Kinesis Streams via Kinesis Data Analytics | KDA supports running SQL queries on streaming data and then store or feed the output to other services (e.g. S3) |
Hands on Lab
(still being written)